1. 목적과 상황
클라이언트에서 온 HttpRequest에 대해서 Exception을 통해 Http status와 Json 코드를 HttpResponse로 반환하고자 한다. 다음 코드와 같이 특정 엔티티 객체를 찾고자 했는데, 못찾았을 경우 orElseThrow()를 통해 특정 Exception을 반환하는 상황이다.
XxxEntity xxxEntity = xxxRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException("xxx.error.not.found"));
CustomException은 여러가지 Exception들을 한 번에 모아놓고 @RestControllerAdvice로 처리하는 클래스 파일 내부에 정의한다.
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomExceptionAdvice {
...
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public CustomMsg customMsgException(WebRequest req, CustomException exception) {
log.error("custom error caused!", exception);
String message = messageSource.getMessage(exception.getFail(), null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
return new CustomMsg(message);
...
}
여기서 ExceptionHandler는 정의하는 클래스에 정의된 내용대로 reponse 객체를 보내고, http status는 HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST인 400을 보내도록 한다.
2. Exception 작성
적용하고자 하는 CustomException 파일을 작성한다. RuntimeException을 상속받도록 하고, String fail 필드 및 생성자를 작성해준다.
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
private final String fail;
public CustomException(String fail) {
super();
this.fail = fail;
}
public CustomException(String fail, String message){
super(message);
this.fail = fail;
}
}
이 내용은 사실 RuntimeException 파일과 같은 형태인데, super()만 추가해주는 것이다.
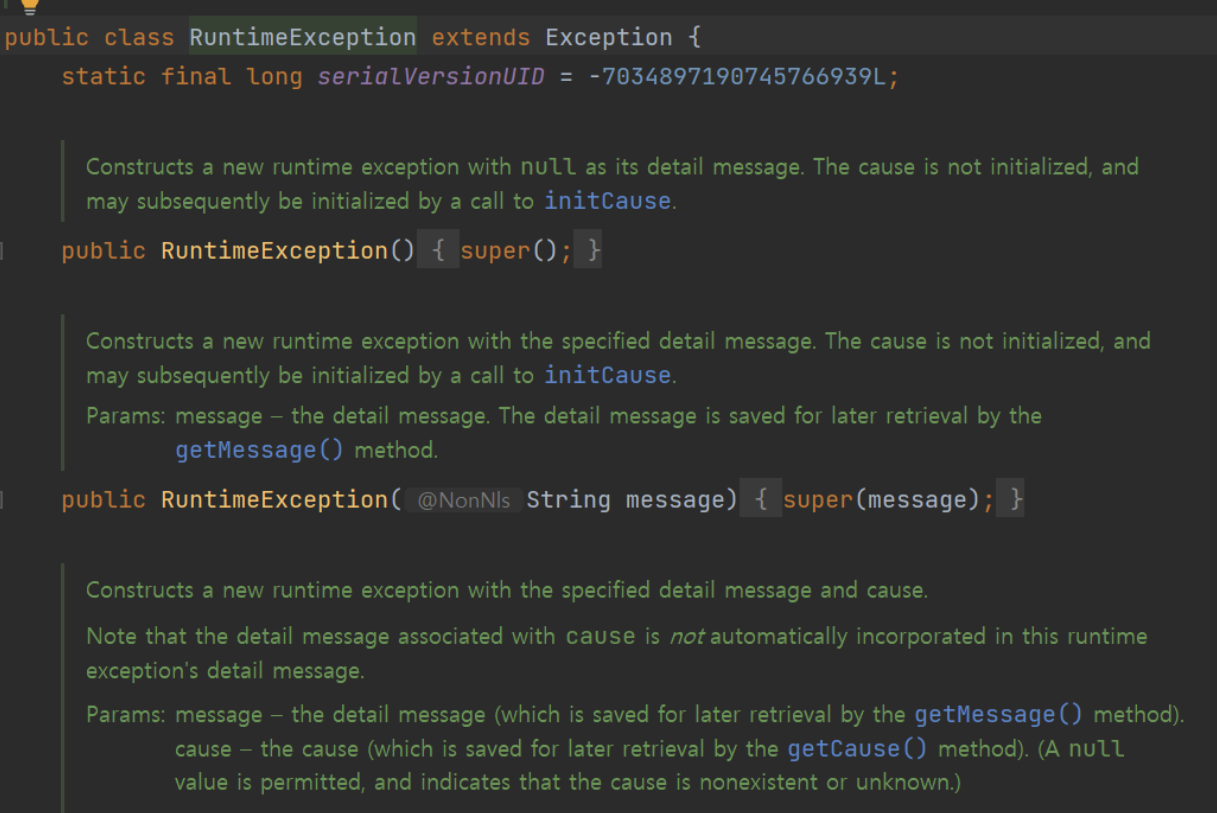
3. Super() 키워드 사용
CustomException의 생성자를 호출하면, 부모 객체인 RuntimeException의 생성자를 '먼저' 실행하게 된다. 따라서 super() 및 super(message)는 부모의 생성자를 호출하는 코드라고 할 수 있다.
상세한 내용은 아래 참조 1)에서 찾아볼 수 있다. 참조 내용에 따르면, 기본 생성자인 super()는 굳이 호출하지 않아도 될 것 같다.
4. 참조
1) 프로그래머스 - 자바 입문 - super와 부모생성자
'Programming-[Backend] > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [스프링 기초] 11. 싱글톤(Singleton) (0) | 2021.06.30 |
|---|---|
| [스프링 기초] 10. Bean Factory와 BeanDefinition (0) | 2021.06.30 |
| [스프링 기초] 9. 빈 조회하기 (0) | 2021.06.15 |
| [스프링 기초] 8. 스프링 컨테이너 (0) | 2021.06.14 |
| [스프링 기초] 7. IoC, DI, 컨테이너 (0) | 2021.06.12 |



